hide
What is a ball float steam trap?
Working of a ball float steam trap
Ball float steam trap specifications
Body material
Sizing
Connection type
Types of ball float steam trap
Loose ball float steam trap
Lever ball float steam trap
Thermostatic air vent ball float steam trap
Applications of ball float steam trap
Advantages of ball float steam trap
Disadvantages of ball float steam trap
Troubleshooting ball float steam trap
leaking live steam
Not discharging condensate
Summary
What is a ball float steam trap?
Ball float steam trap is a mechanical device where a trap works due to steam density difference. In this device, a valve holds a floating trap ball. When the valve body is filled with liquid it makes the ball float on the liquid. An iron rod is used to connect the floating ball to the valve gate so that it can open the valve gate as the ball floats upwards. If the condensate level is low, the valve would be filled with steam. As such, the steam will push the ball downwards closing the gate. Also, the valve can permit steam flow at an adjusted or controlled rate. Ball float steam trap is a device used to separate steam and water. Ball float steam traps are meant to prevent steam wastage. Air and condensate present in steam from a steam plant have certain harmful effects on the effective performance of the plant. Such effects include taking heating space which can be occupied by the steam and also they cause formation of water films on the heating surface or air pockets which limits heat transfer.

Figure: Ball Float Steam Trap.
Working of a ball float steam trap
A ball float steam trap is made up of a valve and a mechanism that opens or closes the valve to drain condensate from the pipe without allowing steam escape. The ball float steam trap is installed at a low point in the system to be drained. Ball float steam trap valve and float are connected in a way that allows the valve to open when the float rises. When the trap is working, steam mixed with water flows through the float chamber. Because water is denser than steam, it falls into the bottom of the trap. This causes the level of water to rise. As such, the rising water level causes the float to lift which then lifts the plug and then opens the valve. This forces the condensate to drain out while the float moves downwards to a lower position which causes the valve to close before the level of condensate is too low to allow steam escape. Through this trap, the condensate that exits the trap gets returned to the feed system.
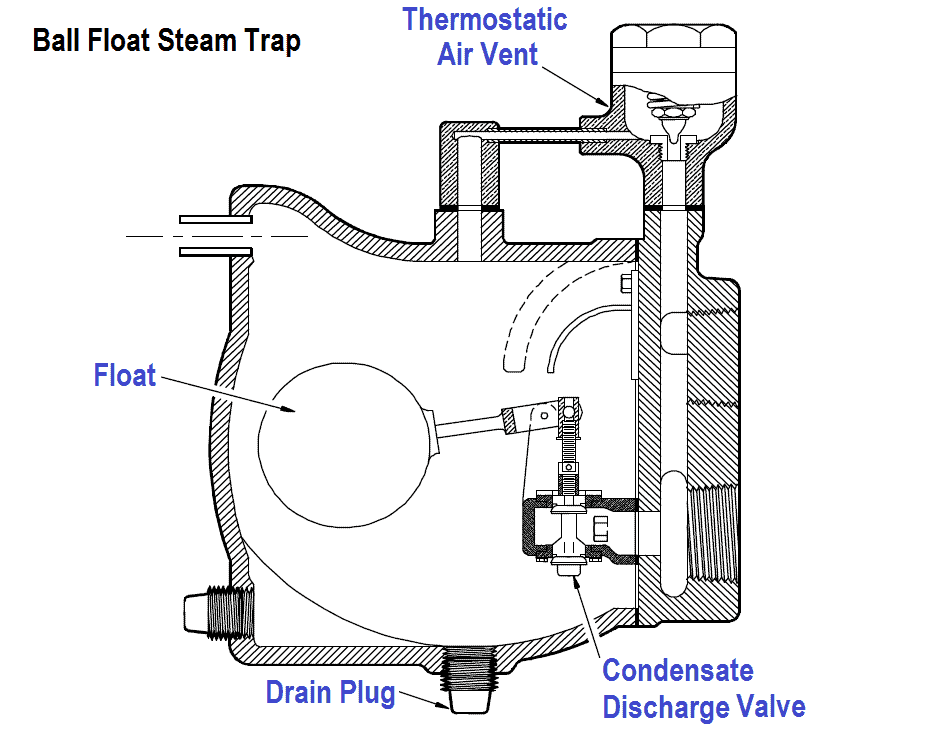
Working of a ball float steam trap
Ball float steam trap specifications
There are factors that affect the minimum ball float steam trap specifications for temperature, pressure, material, discharge capacity, and connection type. Such factors are discussed below.
Body material
Ball float steam trap material is a very important factor to consider when purchasing a trap. The material selection depends on maximum working pressure and temperature at the surrounding environment, condensate discharge location, and requirements for minimal maintenance. Ball float steam trap manufacturers select the material aiming to achieve maximum pressure, pressure test, and piping temperature. The material used to make the ball float steam trap cover, body, and other parts resistant to pressure are not different from those used in other valves. Such materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, ductile cast iron, or gray cast iron. The body material’s maximum applicable temperature and pressure are not always equivalent to the maximum operating temperature and pressure of a ball float steam trap. This is because the maximum working temperature and pressure can be restricted by the temperature/pressure resistance of other components like gaskets and internal parts.
Sizing
A ball float steam trap needs to match the size of the pipeline on the outlet of the device supplying the condensate to that trap. Condensate pipeline on the discharge of equipment supplying condensate to the trap need to be sized following the details in the table below. The ball float trap need not be sized less than the outlet pipe of the equipment since this can result in waterlogging and damage or heating problems. Also, pipe size at the outlet of the ball float steam trap need not depend on trap size but rather be designed to produce the needed flow rate and restrict the loss of pressure for a two-phase flow.
Connection type
Most users of steam need threaded, flanged, or socket-welded ball float steam trap for connections based on the standard national, company, or industry specifications and codes. Threaded connections are cheaper relative to flanged connections. However, threaded connections have to be screwed in when installing meaning that the trap outlet pipe has to be disconnected or use a union to enhance easier trap replacement. When using threaded connections on ball float steam trap, threads used must follow official standards to reduce poor connections on the connected pipeline. Ball float steam trap with socket weld connection is at a time preferred in certain steam plants to restrict the level of steam leakage. However, these connections are difficult to uninstall during replacement and they tend to have higher maintenance costs. Ball float steam trap with a flanged connection is easy to remove and replace if the trap has equal size and dimensions face to face. After the trap specifications have been done as per the environment and operating conditions the next approach is to determine the appropriate discharge capacity and factor of safety.
Types of ball float steam trap
Loose ball float steam trap
The simple type of a ball float steam trap is a loose float trap. This trap is shown in the figure below. The condensate enters the ball float steam trap via the inlet at point A. This causes a level of water to rise and the float at B is lifted off from point C. This makes way for the condensate to pass flow freely via the valve orifice at D. When the condensate flow is diminished, the level of water in the ball float steam trap falls and the ball starts to cover the exit point D. After discharging all the condensate, the ball covers the orifice and thus it prevents loss of steam. The float action helps to enhance continuous discharge to be maintained relative to the quantity of condensate reaching the ball float steam trap. This type of loose ball float steam trap is advantageous in that it requires little maintenance as it has no working components to go wrong. However, loose ball float steam trap the outlet is kept lower than the inlet. This design results in a water seal that restricts steam blowing via the trap. Also, this seal does not discharge air from the trap via the main orifice. As such, another hand air cock point E has to be included. The other problem associated with a loose ball float steam trap is that it is difficult to achieve a good seating of the ball on a small outlet hole.
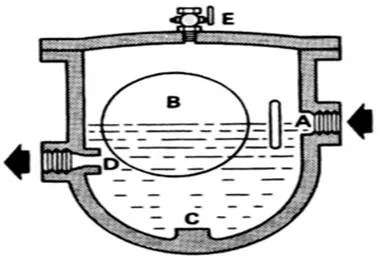
Figure: Loose ball float steam trap.
Lever ball float steam trap
This is a type of ball float steam trap where condensate enters the body via inlet A and ball B gets lifted when the level of water rises. The ball is connected to the outlet valve at point D by use of float arm point C. The outlet valve opens since the condensate lifts the ball. The valve position changes as per the water level in the body which gives continuous discharge of condensate on any load that falls in the maximum capacity of this type of trap. When the condensate load is diminished steam raises to reach the trap, the float drops to its lower position. The valve is fixed against the seat to avoid steam waste. The one main problem associated with this trap is that it cannot discharge via the main valve as it starts.
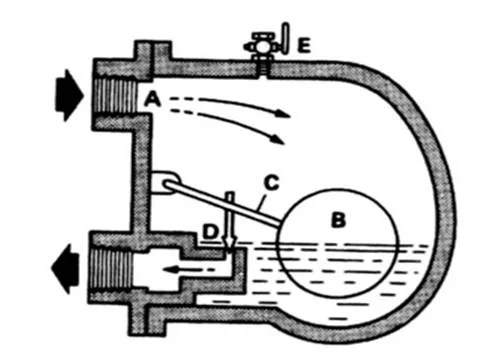
Lever ball float steam trap
Unless the ball float steam trap manufacturers provide a certain mechanism to release air from the system, then it will prevent condensate to flow into the trap making it air-bound. Lever ball float steam trap manufacturers will sometimes design the trap with a manual cock at point E. However, this manual cock requires to be operated manually every time steam is switched on.
Thermostatic air vent ball float steam trap
This is a ball float steam trap with an automatic air vent instead of a manual cock as for the lever ball float steam trap. The air vent is located in the space of the steam above the level of the condensate. After initial air is released, it gets closed until air and other non-condensable gases collect during normal operation causing it to open and thus reduce steam/air temperature mixture. This type of thermostatic air vent ball float steam trap is advantageous in that it increases the capacity of the condensate on cold start-up.
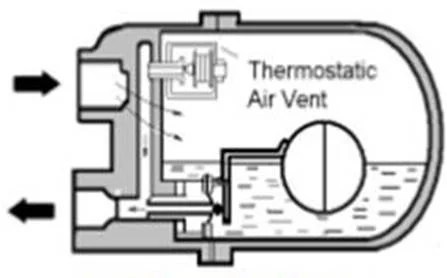
Thermostatic air vent ball float steam trap
Applications of ball float steam trap
- Used in a heat exchanger to enhance heat transfer.
- They are used in heating ovens.
- Heater batteries and unit heaters.
- Separator drainages.
- Used in drying cylinders.
- Heating tanks.
- Heating presses to transfer heat to a surface.
Advantages of ball float steam trap
- Discharge condensate immediately irrespective of steam pressure changes, especially where an automatic air vent is used.
- Discharge condensate continuously at steam temperatures. As such, it is the first choice for use where the heat transfer rate is high when heating the surface area available.
- Handle light and heavy condensate loads and it is not affected by sudden and wide pressure fluctuations or flow rate.
- Resistant to water hammers.
- These traps can discharge air freely especially when an automatic air vent is used.
- Ball float steam trap manufacturers design them with a large capacity for a variety of applications.
Disadvantages of ball float steam trap
- Dusceptible to damage by excessive freezing.
- These traps require various internal parts to allow working over various pressure ranges.
- If these traps are subjected to high differential pressure than the design pressure range they can close and pass no condensate.
Troubleshooting ball float steam trap
leaking live steam
- Dirt was deposited on the valve seat. Put a separate strainer before the ball float steam trap. Ensure the strainer is properly removed and cleaned. Be inspecting the spindle and seat for any dirt deposition and cleaning the surface.
Not discharging condensate
- Ball float punctured. This will make the float full of water and thus it will lose its buoyancy and thus ball will not rise to float on water. This will make the trap choke. This needs to replace the float ball with another one.
- Low differential pressure. Low differential pressure can easily be nullified by backpressure. As such, the ball float trap will not discharge any condensate. To avoid this ensure that the differential pressure is kept high as recommended.
Summary
A ball float steam trap is a type of mechanical steam trap. This trap is used to separate steam and water. A ball float steam trap works by opening a valve to allow fluid flow. At the same time, the trap prevents steam from escaping. A ball float steam trap helps to ensure steam is not wasted. A ball float steam trap is made up of two elements valve and seat assembly. The valve offers a variable orifice where condensate becomes discharged to. The second element helps to close or open the valve that determines if fluid is to be discharged or not. The separation of fluid is done by applying the concept of density difference. The ball float steam trap helps to separate the water and steam because the water is denser than the steam. This trap uses a floating ball. When the trap is full of liquid the ball floats on it. The floatation of the ball opens a valve gate to allow the condensate to flow. When the condensate level is very low, the trap would become full of steam. Consequently, the steam pushes the ball downwards to close the gate valve.
Three types of ball float steam traps are the thermostatic air vent ball float steam trap, the lever ball float steam trap, and the loose ball float steam trap. These traps are used in many applications such as heating presses, heating tanks, heat exchangers, drying cylinders among others. The ball float steam traps are preferred due to their properties such as resistance to water hammer, large capacity, ability to discharge condensate at steam temperature, ability to discharge condensate as soon as it is formed.